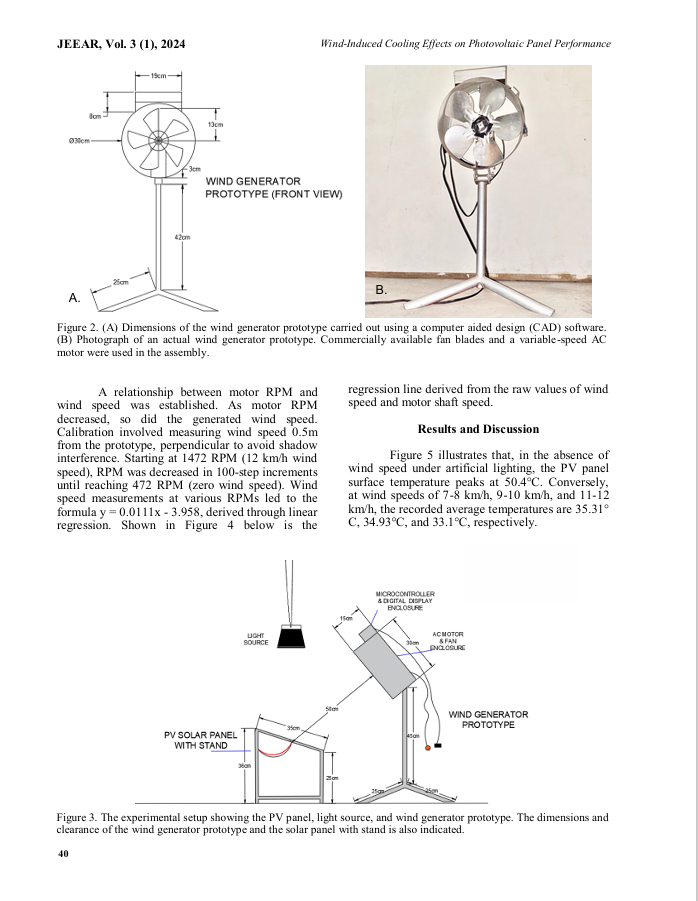
Wind-Induced Cooling Effects on Photovoltaic Panel Performance
Abstract
This investigation evaluated the performance of a photovoltaic (PV) panel system under varied cooling speeds of a calibrated wind generator. The objectives encompassed the calibration of wind speed, integration of the wind generator with the PV panel system, monitoring the performance of the PV panel with wind-induced cooling, and analyzing overall performance under different wind generator settings. Parameters assessed included open circuit voltage, short circuit current, PV panel surface temperature, and power output. The tests were carried out both with and without wind cooling and under artificial and natural lighting conditions. Under artificial lighting conditions, the solar PV panel demonstrated suboptimal short circuit current compared to natural lighting conditions, leading to an overall decrease in power output. Moreover, the findings revealed a significant relationship between simulated wind speed and the overall performance of the PV panel, with notable variations in surface temperature, voltage level, current level, and power output. The statistical analysis supported these findings, with all dependent variables exhibiting statistically significant differences. The practical implications of these observations are pertinent to the design of more efficient and sustainable PV and PV-wind cooling systems. By comprehending the influence of wind on PV panel performance, system designers and operators can make informed decisions to maximize energy production and enhance the overall efficiency of the PV system.