Physico-chemical and Bacteriological Water Quality Evaluation of the Four Tributaries in Mt. Matutum Protected Landscape (MMPL), South Cotabato, Philippines
Abstract
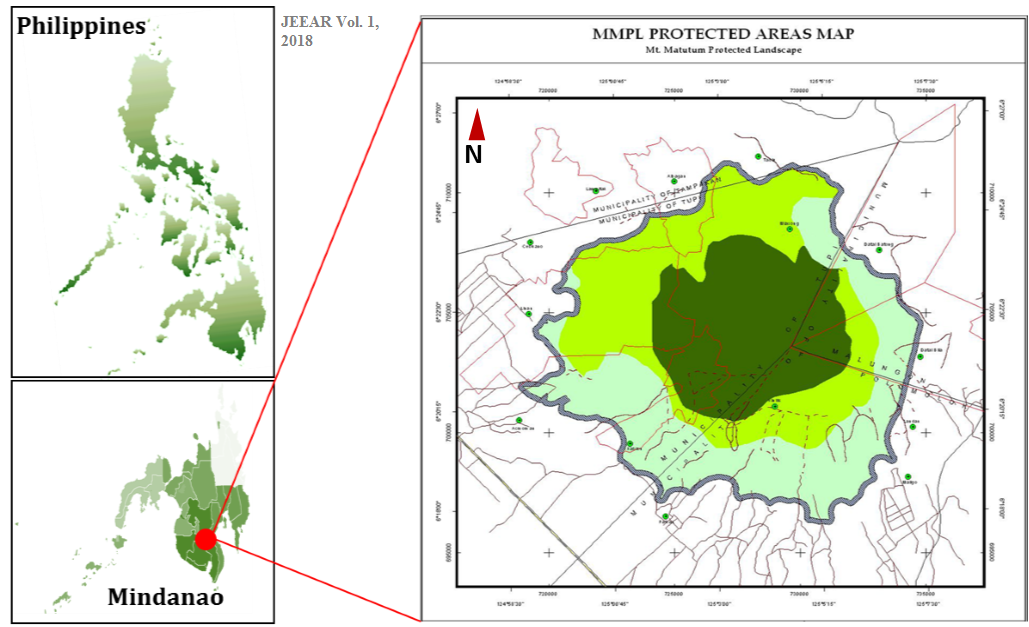
Healthy riverine systems provide ecological services that can be translated into human use and consumption. However, human activities cause environmental degradation limiting available pristine water supply and raising public health concerns. In the present study, four tributaries surrounding Mt. Matutum Protected Landscape (MMPL) were selected (Glandang, Linan, Kawit, and Amlok) for evaluation of their physicochemical and microbial characteristics between wet and dry season. The pH and total dissolved solids (TDS) of the river waters ranged from 6.75-8.68 and 55.96-221.89 ppm, respectively, with a pronounced pH fluctuation and TDS increase in Glandang and Linan tributaries from upstream to downstream stations. All tributaries showed varying dissolved oxygen (DO) levels upstream but become relatively stable downstream. All DO values, however, are below the standard limit set for freshwater quality. In terms of microbial load, total coliform ranged from 51-275 cfu/ml while E. coli showed absence (0 cfu/ml) to as high as 77 cfu/ml. Higher total coliform counts were observed on Kawit and Amlok tributaries which are situated in areas that are relatively more forested than the other two rivers. Presence of E. coli was also detected in the water samples from all tributaries. Temporal variation is significant indicating increased pH, TDS and microbial load during the wet season and DO during the dry season. The present microbial load of the four tributaries would restrict the utilization of water resource and necessitate proper treatments prior to domestic use.
Read full article here.